 the induction
furnace is mainly used for making
steel and consist of devices like refractory-lined vessel and
electrodes. electrodes are normally round in section and comes in
segments with threaded couplings, so that as the electrodes wear, new
segments can be added. the arc forms between the charged material and
the electrode. the charge so formed is heated both by current passing
through the charge and by the radiant energy evolved by the arc.
the induction
furnace is mainly used for making
steel and consist of devices like refractory-lined vessel and
electrodes. electrodes are normally round in section and comes in
segments with threaded couplings, so that as the electrodes wear, new
segments can be added. the arc forms between the charged material and
the electrode. the charge so formed is heated both by current passing
through the charge and by the radiant energy evolved by the arc.
did you know?
induction heating process is a method in which the electrical
conducting material is heated through by eddy currents induced by a
varying electromagnetic field. the principle of the induction
heating furnace is similar to that of a transformer.
|
this type of furnace is widely used in latest foundries
especially iron where now couplas are replaced by induction furnaces to
melt cast iron. the use of couplas result in the emission of lots of
dust and other pollutants but the use of induction furnace has minimized
this problem to a larger extent. induction heating furnace comes in
various sizes and configuration. however induction furnace has it's own
limitation. the induction process used in foundries lacks refining
capacity. charge materials must be clean of oxidation products and of a
known composition, and some alloying elements may be lost due to
oxidation (and must be re-added to the melt).
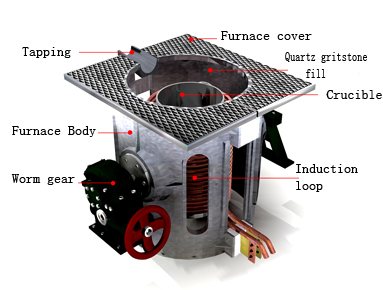
 induction furnace capacities range from less than one kilogram to one
hundred tonnes capacity, and are used to melt iron and steel, copper,
aluminum, and precious metals. the one major drawback to induction
furnace usage in a foundry is the lack of refining capacity; charge
materials must be clean of oxidation products and of a known
composition, and some alloying elements may be lost due to oxidation
(and must be re-added to the melt).
induction furnace capacities range from less than one kilogram to one
hundred tonnes capacity, and are used to melt iron and steel, copper,
aluminum, and precious metals. the one major drawback to induction
furnace usage in a foundry is the lack of refining capacity; charge
materials must be clean of oxidation products and of a known
composition, and some alloying elements may be lost due to oxidation
(and must be re-added to the melt).
the frequency of operation of induction furnace also vary. usually it
depend on the material being melted, the capacity of the furnace and the
melting speed required. a high frequency furnace is usually faster to
melt a charge whereas lower frequencies generate more turbulence in the
metal, reducing the power that can be applied to the melt.
when the induction furnace operates it emits a hum or whine (due to
magnetostriction), the pitch of which can be used by operators to
identify whether the furnace is operating correctly, or at what power
level.
features
following are the features of induction furnace:
- highest chemical durability.
- lowest alloy losses.
- leading to highest metal quality with respect to impurities.
- high refractoriness.
- available in various sizes.
- comes in different capacities.
applications
these furnace are designed from various applications. for applications
such as adhesive curing and paint drying, the parts are simply inserted
into the heating chamber and the furnace is activated. following are the
application of induction furnace:
- curing
- drying
- copper
- brazing
- soldering
- melting
- stainless steel
- iron castings
- foundries
title |
unit |
gwt-
0.15ton |
gwt-
0.3ton |
gwt-
0.5ton |
gwt-
1ton |
gwt-
1.5ton |
gwt-
2ton |
gwt-
3ton |
equipment
rating power |
kw |
100 |
160 |
250 |
500 |
750 |
1000 |
1500 |
input voltage |
v |
380 |
380 |
380 |
660 |
380 |
660 |
380 |
660 |
380 |
575-1250 |
melting rate |
kg/hour |
160 |
300 |
490 |
1120 |
1680 |
2300 |
3300 |
equipment
water rate |
ton/hour |
5 |
5 |
8 |
10 |
22 |
28 |
35 |
| |
kwh/ton |
850 |
800 |
750 |
700 |
650 |
650 |
650 |
| |
v |
750 |
750 |
1500 |
1400-2500 |
1400-2500 |
1400-2500 |
2300-2500 |
furnace
rating capacity |
ton |
0.15 |
0.3 |
0.5 |
1 |
1.5 |
2 |
3 |
match cover
transformer |
kva |
125-160 |
160-200 |
250-315 |
500-630 |
800-1000 |
1000-1250 |
1600-2000 |
rating
temperature |
'c |
1250 |
1250 |
1250 |
1250 |
1250 |
1250 |
1250 |
furnace body inside pathway |
meter |
φ0.72×0.8 |
φ0.87×0.9 |
φ1.1×1.1 |
φ1.26×1.3 |
φ1.26×1.4 |
φ1.38×1.6 |
φ1.58×1.72 |
capacitor |
kvar |
4000 |
6000 |
8000 |
16000
|
32000
|
24000
|
48000
|
32000
|
64000
|
48000 |
note:gwt-1t, gwt-1.5t, gwt-2t input power 380v,capacitor capacity double.
<<back